Characteristics of the transcription genome and the development of microsatellites (SSR) molecular markers used in analyzing genetic diversity in populations and species of Ginseng Ngoc Linh (Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv) in Vietnam
11/08/2020Sam Ngoc Linh Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv. is an important herb, endemic and endangered in Vietnam. Understanding the importance of the genetic diversity of endangered species remaining in the forest is essential to developing effective species conservation, restoration and management strategies. However, the diversity and genetic structure of the Ngoc Linh ginseng species are not fully understood due to the lack of specific molecular markers.
In this study, we conducted the following studies: (1) decoding the entire transcription genome of Ngoc Linh P. vietnamensis by Illumina HiSeq ™ 4000 technique and genetic function analysis, classification metabolic pathways based on the traits of the transcription genome; (2) then we built a molecular marker EST-SSR for Ngoc Linh ginseng; (3) demonstrate the effectiveness of these markers through studying the diversity and genetic structure of three wild populations of Ngoc Linh ginseng and (4) evaluate the effects of geographic distance on the level of Genetically modified wild populations were studied.
After rigorous data assembly, correction, quality control and screening from the raw data set of 23,741,783 nucleotide sequences, 89,271 sequences were found to contain 89,271 genetic units of medium length. bottle 589,31bp. 31,686 genetic units were annotated in 7 different databases (Gene Ontology (GO), protein sequences (NR), Swiss-Prot, Pfam, Clusters of Orthologous Groups (COG), Karyotic Orthologous Groups of proteins (KOG) ), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)). Next, 11,343 segments containing EST-SSR were discovered. From 7,774 designed SSR primer pairs, 110 pairs were randomly selected to test for polymorphic specificity, in which 20 primer pairs successfully replicated DNA fragments. Using 9 pairs of polymorphic SSR primers to analyze the structure and genetic diversity of Sam Ngoc Linh population.
The results showed a high level of genetic diversity in the population, including: mean observed heterozygous gene coefficient (Ho) = 0.422 and expected heterozygous gene coefficient (He) = 0.479. Use two models TPM (Two-phase Mutation Model) and SMM (Stepwise Mutation Model) in Bottleneck analysis for found: study populations are significantly deficient in heterozygous genes (p <0.01). This was shown in the bottleneck in all study populations. Genetic differences between populations were moderate (Fst = 0.133) and insignificantly high levels of gene flow exchange (Nm = 1.63) between populations. Analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) showed that 63.17% variation in individuals and 12.45% in populations. Our results show that two genetic clusters are related to geographical distance. The results of this study not only provide a scientific basis for the propagation of Ngoc Linh ginseng, but also serve as a basis for preserving and maintaining genetic diversity of populations and species.
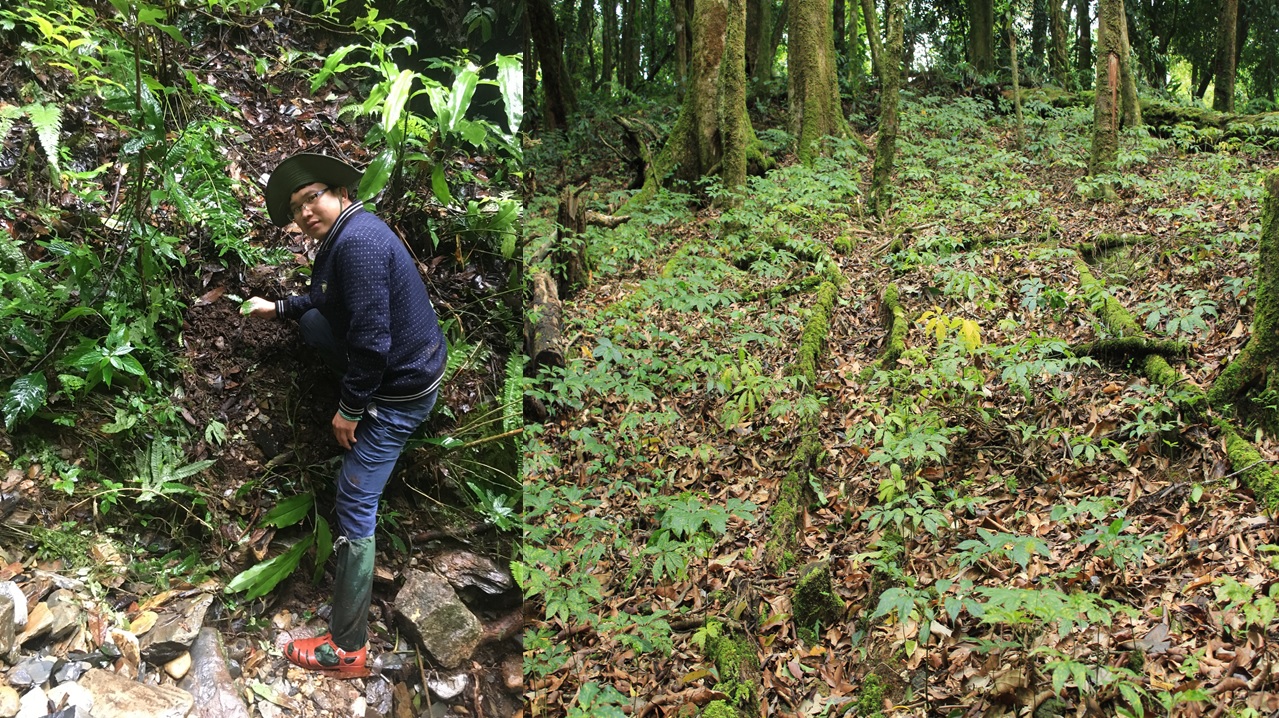


Image of jade ginseng used in research
Document source:
Dinh Duy Vu, Syed Noor Muhammad Shah, Mai Phuong Pham, Van Thang Bui, Minh Tam Nguyen, Thi Phuong Trang Nguyen. De novo assembly and Transcriptome characterization of an endemic species of Vietnam, Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv., Including the development of EST-SSR markers for population Genetics. BMC Plant Biology (2020) 20: 358. (SCIE, Q1, Impact factor: 3.83)
https://bmcplantbiol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12870-020-02571-5
Vu Dinh Duy/Institute of Tropical Ecology